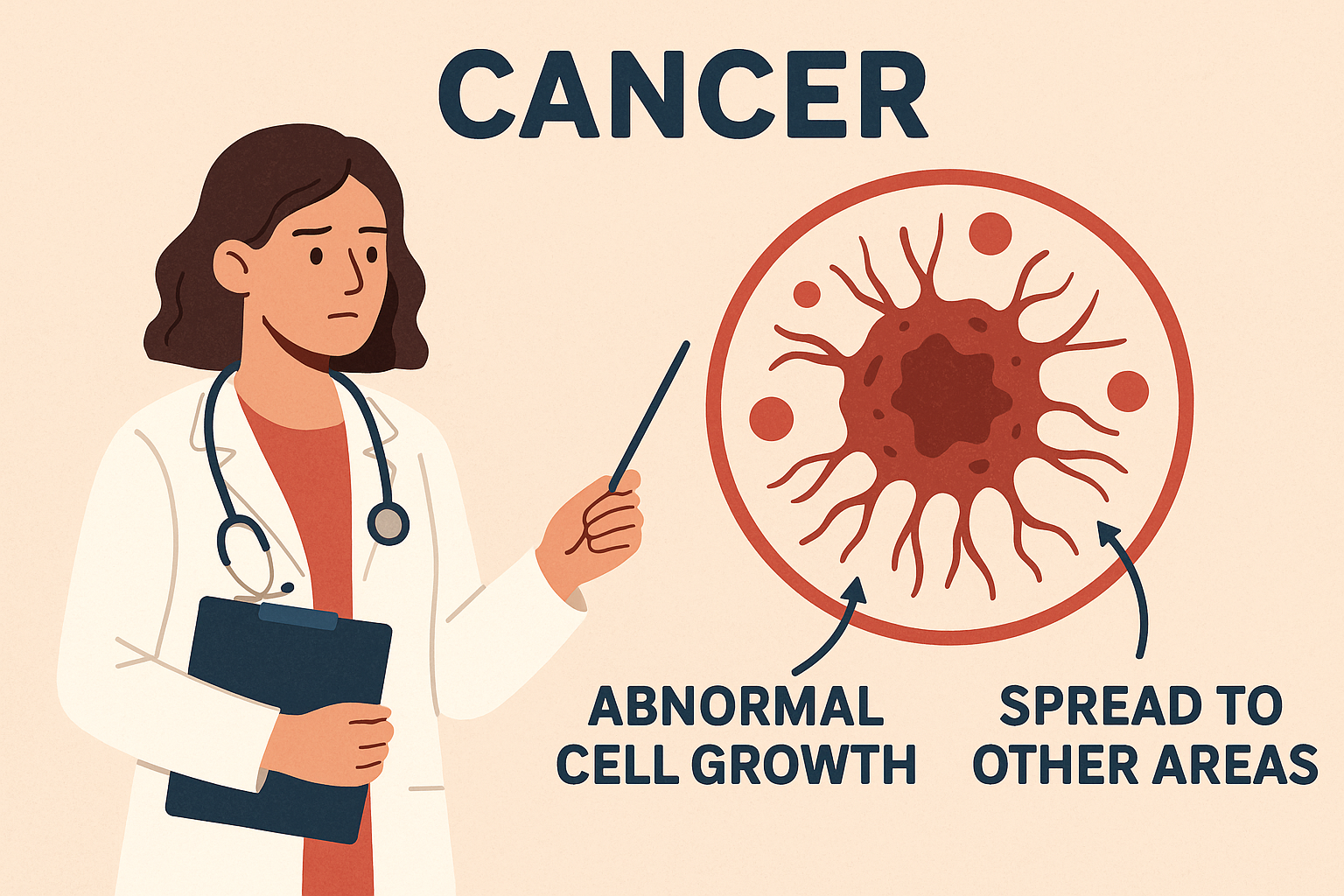
Cancer is a complex group of diseases characterized by the uncontrolled growth and spread of abnormal cells. If not controlled, it can lead to death. Understanding the early signs and treatment options is crucial for better outcomes.

Common Symptoms of Cancer
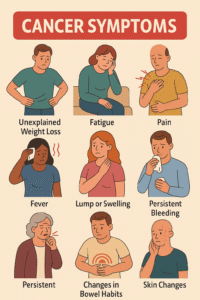
Cancer symptoms vary depending on the type and location of the cancer. However, some general symptoms may include:
- Unexplained Weight Loss: A sudden drop in weight without changes in diet or exercise.
- Fatigue: Persistent tiredness that does not improve with rest.
- Pain: Constant or severe pain, particularly if unexplained.
- Fever: Frequent fevers without an obvious cause.
- Skin Changes: Darker looking skin (hyperpigmentation), yellowish skin and eyes (jaundice), redness, itching, or excessive hair growth.
- Changes in Bowel or Bladder Habits: Prolonged constipation, diarrhea, or changes in stool appearance.
- Unusual Bleeding or Discharge: Blood in urine, stool, coughing up blood, or unusual vaginal bleeding.
- Lumps or Thickening: New lumps or thickening in the breast, testicles, lymph nodes, or elsewhere.
Early detection often significantly increases the chances of successful treatment.
How Cancer is Diagnosed
- Medical History and Physical Exam: Initial step involving discussion of symptoms and a physical check.
- Laboratory Tests: Blood, urine, and other fluid analyses.
- Imaging Tests: X-rays, CT scans, MRIs, ultrasounds, and PET scans help locate tumors.
- Biopsy: The removal of a small tissue sample for examination under a microscope.
Treatment Options
Treatment depends on the type and stage of cancer, among other factors.
- Surgery: Removes cancerous tissue from the body.
- Radiation Therapy: Uses high-energy rays to kill or shrink cancer cells.
- Chemotherapy: Involves using drugs to kill cancer cells.
- Immunotherapy: Boosts the body’s natural defenses to fight cancer.
- Targeted Therapy: Focuses on specific molecules involved in cancer growth.
- Hormone Therapy: Blocks or removes hormones that fuel certain cancers.
- Stem Cell Transplant: Restores blood-forming stem cells in cancer patients.
Living with Cancer
A cancer diagnosis is life-altering. Support from healthcare teams, counselors, family, and support groups is essential. Advances in treatment have significantly improved survival rates and quality of life for many cancer patients.

Nutrition and Activities to Help Fight Cancer
Maintaining a healthy diet and engaging in regular physical activities can support cancer treatment and improve overall well-being. Some recommendations include:
- Plant-Based Diet: Focus on fruits, vegetables, whole grains, legumes, and nuts.
- Lean Proteins: Include sources like fish, chicken, tofu, and legumes.
- Healthy Fats: Prefer olive oil, avocado, and nuts over saturated fats.
- Limit Sugar and Processed Foods: Reduce intake of sugary drinks, fast foods, and processed snacks.
- Hydration: Drink plenty of water to support bodily functions.
- Physical Activities: Moderate activities like walking, swimming, yoga, and light strength training can enhance physical and mental health.
- Stress Management: Practices like meditation, deep-breathing exercises, and mindfulness can reduce stress levels.
- Adequate Rest: Ensure sufficient sleep and relaxation periods to support recovery.
Don’t forget to follow our page for diseases and treatments.